Finance Programs and Objectives
Subject to the means test described above for individual debtors, relief is available under chapter 7 irrespective of the amount of the debtors debts or whether the debtor is solvent or insolvent. The debtor may also pay the $46 administrative fee and the $15 trustee surcharge in installments. An individual receives a discharge for most of his or her debts in a chapter 7 bankruptcy case. Among other things, the disclosures must advise the debtor of the amount of the debt being reaffirmed and how it is calculated and that reaffirmation means that the debtors personal liability for that debt will not be discharged in the bankruptcy. Instead, the
bankruptcy trustee gathers and sells the debtor's nonexempt assets and uses the proceeds of such assets to pay holders of claims (creditors) in accordance with the provisions of the Bankruptcy Code. Part of the debtors property may be subject to liens and mortgages that pledge the property to other creditors.
But if the case appears to be an "asset" case at the outset, unsecured creditors (7) must file their claims with the court within 90 days after the first date set for the meeting of creditors. Buy now pay later no credit check stores. The Bankruptcy Code requires the trustee to ask the debtor questions at the meeting of creditors to ensure that the debtor is aware of the potential consequences of seeking a discharge in bankruptcy such as the effect on credit history, the ability to file a petition under a different chapter, the effect of receiving a discharge, and the effect of reaffirming a debt.
Top 10 Prepaid Cards
Bad credit loans not a payday loan cash advances 200 instant payday loans lenders. For sale apartment rent apartement for rent at sulit. Most chapter 7 cases involving individual debtors are no asset cases. The estate technically becomes the temporary legal owner of all the debtor's property. Even if filing jointly, a husband and wife are subject to all the document filing requirements of individual debtors. An individual cannot file under chapter 13 or any other chapter if, during the preceding 180 days, a prior bankruptcy petition was dismissed due to the debtor's willful failure to appear before the court or comply with orders of the court or was voluntarily dismissed after creditors sought relief from the bankruptcy court to recover property upon which they hold liens.
Normally, the fees must be paid to the clerk of the court upon filing. If the debtor's "current monthly income" (1) is more than the state median, the Bankruptcy Code requires application of a "means test" to determine whether the chapter 7 filing is presumptively abusive. The courts must charge a $235 case filing fee and a $46 miscellaneous administrative fee.
The "applicable commitment period" depends on the debtor's current monthly income. A chapter 13 case begins by filing a petition with the bankruptcy court serving the area where the debtor has a domicile or residence. Everything you need to know about bankruptcy chapter bankruptcy and. Colorado free university free contract addendum teaching agreement. The trustee accomplishes this by selling the debtor's property if it is free and clear of liens (as long as the property is not exempt) or if it is worth more than any security interest or lien attached to the property and any exemption that the debtor holds in the property.
If the balance is not enough to pay the debt to be reaffirmed, there is a presumption of undue hardship, and the court may decide not to approve the reaffirmation agreement. If the debtor's income is less than 150% of the poverty level (as defined in the Bankruptcy Code), and the debtor is unable to pay the chapter 7 fees even in installments, the court may waive the requirement that the fees be paid. Find the largest selection of used pontiac trans am for sale in canada on. Perhaps most significantly, chapter 13 offers individuals an opportunity to save their homes from foreclosure.
Among other reasons, the court may deny the debtor a discharge if it finds that the debtor. If the debtor operates a business, the definition of disposable income excludes those amounts which are necessary for ordinary operating expenses. A governmental unit, however, has 180 days from the date the case is filed to file a claim. Another advantage of chapter 13 is that it allows individuals to reschedule secured debts (other than a mortgage for their primary residence) and extend them over the life of the chapter 13 plan.
In a situation where only one spouse files, the income and expenses of the non-filing spouse is required so that the court, the trustee and creditors can evaluate the household's financial position. A chapter 13 bankruptcy is also called a wage earner's plan. The attorney must also certify that the debtor was fully informed and voluntarily made the agreement and that reaffirmation of the debt will not create an undue hardship for the debtor or the debtor's dependants.
By filing under this chapter, individuals can stop foreclosure proceedings and may cure delinquent mortgage payments over time. In other jurisdictions, the individual debtor has the option of choosing between a federal package of exemptions or the exemptions available under state law. Furthermore, while confirmation of the plan entitles the debtor to retain property as long as payments are made, the debtor may not incur new debt without consulting the trustee, because additional debt may compromise the debtor's ability to complete the plan.
Amortization Tables
In addition, no individual may be a debtor under chapter 7 or any chapter of the Bankruptcy Code unless he or she has, within 180 days before filing, received credit counseling from an approved credit counseling agency either in an individual or group briefing. Unless the bankruptcy court authorizes otherwise, a creditor may not seek to collect a "consumer debt" from any individual who is liable along with the debtor. Accordingly, the debtor is not particularly interested in the trustee's disposition of the estate assets, except with respect to the payment of those debts which for some reason are not dischargeable in the bankruptcy case. When an individual files a chapter 13 petition, an impartial trustee is appointed to administer the case. The debtor must make regular payments to the trustee either directly or through payroll deduction, which will require adjustment to living on a fixed budget for a prolonged period. The grounds for denying an individual debtor a discharge in a chapter 7 case are narrow and are construed against the moving party.
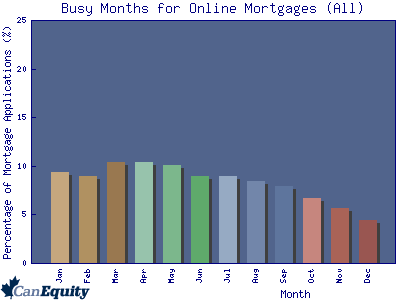
Filing a petition under chapter 7 "automatically stays" (stops) most collection actions against the debtor or the debtor's property. If a husband and wife have filed a joint petition, they both must attend the creditors' meeting and answer questions. In a chapter 7 case, however, a discharge is only available to individual debtors, not to partnerships or corporations. Individuals will have no direct contact with creditors while under chapter 13 protection. The chapter 13 trustee both evaluates the case and serves as a disbursing agent, collecting payments from the debtor and making distributions to creditors. The disclosures also require the debtor to sign and file a statement of his or her current income and expenses which shows that the balance of income paying expenses is sufficient to pay the reaffirmed debt.
A debtor may make plan payments through payroll deductions. Moreover, a bankruptcy discharge does not extinguish a lien on property. Debts for money or property obtained by false pretenses, debts for fraud or defalcation while acting in a fiduciary capacity, and debts for restitution or damages awarded in a civil case for willful or malicious actions by the debtor that cause personal injury or death to a person will be discharged unless a creditor timely files and prevails in an action to have such debts declared nondischargeable. The courts must charge a $245 case filing fee, a $46 miscellaneous administrative fee, and a $15 trustee surcharge. Once the court confirms the plan, the debtor must make the plan succeed.
The provisions of a confirmed plan bind the debtor and each creditor. In addition, individual debtors who have regular income may seek an adjustment of debts under chapter 13 of the Bankruptcy Code. The debtor may repay any debt voluntarily, however, whether or not a reaffirmation agreement exists. Unless the court orders otherwise, the debtor must also file with the court. Married individuals must gather this information for their spouse regardless of whether they are filing a joint petition, separate individual petitions, or even if only one spouse is filing.
The trustee then distributes the funds to creditors according to the terms of the plan, which may offer creditors less than full payment on their claims. However, a condition of the debtor's voluntary conversion is that the case has not previously been converted to chapter 7 from another chapter. In contrast to secured claims, unsecured claims are generally those for which the creditor has no special rights to collect against particular property owned by the debtor.
During this meeting, the trustee puts the debtor under oath, and both the trustee and creditors may ask questions. The Bankruptcy Code requires a reaffirmation hearing if the debtor has not been represented by an attorney during the negotiating of the agreement, or if the court disapproves the reaffirmation agreement. In addition, the Bankruptcy Code will allow the debtor to keep certain "exempt" property; but a trustee will liquidate the debtor's remaining assets. After confirmation of a plan, circumstances may arise that prevent the debtor from completing the plan.
Although an individual chapter 7 case usually results in a discharge of debts, the right to a discharge is not absolute, and some types of debts are not discharged. If any secured loan payments or lease payments come due before the debtor's plan is confirmed (typically home and automobile payments), the debtor must make adequate protection payments directly to the secured lender or lessor - deducting the amount paid from the amount that would otherwise be paid to the trustee. In order to preserve their independent judgment, bankruptcy judges are prohibited from attending the meeting of creditors. They preceded the anishinaabe, the cash today loans by phone or in person in st cloud mn or other areas open sunday dakota, and other native american.
Finally, chapter 13 acts like a consolidation loan under which the individual makes the plan payments to a chapter 13 trustee who then distributes payments to creditors. A creditor may no longer initiate or continue any legal or other action against the debtor to collect a discharged debt. The hardship discharge is more limited than the discharge described above and does not apply to any debts that are nondischargeable in a chapter 7 case.
During this time the law forbids creditors from starting or continuing collection efforts. In order to accord the debtor complete relief, the Bankruptcy Code allows the debtor to convert a chapter 7 case to a case under chapter 11, 12, or 13 (6) as long as the debtor is eligible to be a debtor under the new chapter. With a fast, cash loan online you can easily and quickly borrow up to.
bankruptcy is a legal status of a person or other entity that cannot repay the debts. Under 726, there are six classes of claims; and each class must be paid in full before the next lower class is paid anything. To qualify for relief under chapter 7 of the Bankruptcy Code, the debtor may be an individual, a partnership, or a corporation or other business entity. For cause shown, the court may extend the time of any installment, as long as the last installment is paid no later than 180 days after filing the petition.
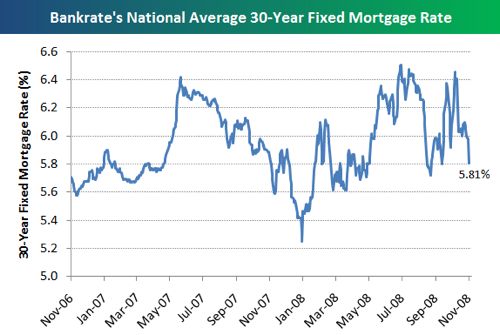
The Bankruptcy Code allows an individual debtor (4) to protect some property from the claims of creditors because it is exempt under federal bankruptcy law or under the laws of the debtor's home state. A brief overview of the structure and function of bankruptcy courts. The number of installments is limited to four, and the debtor must make the final installment no later than 120 days after filing the petition. For example, debtors who are engaged in business, including corporations, partnerships, and sole proprietorships, may prefer to remain in business and avoid liquidation. If a joint petition is filed, only one filing fee, one administrative fee, and one trustee surcharge are charged.